Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) are a vital instrument for addressing infrastructure gaps and promoting economic growth. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of PPPs. The guide outlines their advantages and disadvantages, provides real-life examples of public-private partnerships, and discusses their role in real estate development. Furthermore, exploring the different facets of PPPs provides a thorough understanding of their importance, benefits, and challenges.
What are Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)?
A Public-Private Partnership (PPP) is a contractual arrangement between a public agency (government) and a private entity. Through this agreement, the skills and assets of each sector (public and private) share in delivering a facility for public use. Consequently, the primary goal of a PPP is to combine the best of both worlds. It leverages the private sector’s resources and expertise to improve infrastructure.
Types of PPPs
There are various types of PPPs, including:
1. Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT): The private partner builds and operates the facility for a specified period before transferring ownership to the public partner.
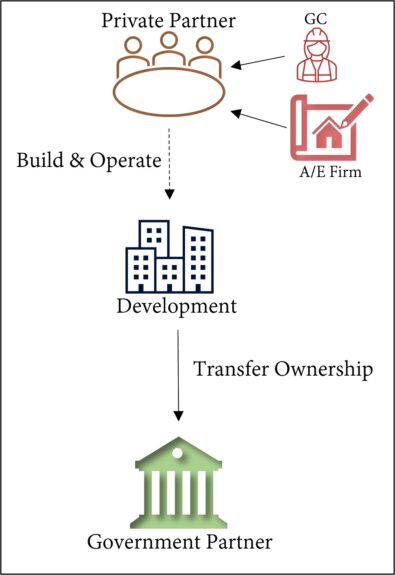
2. Design-Build-Finance-Operate (DBFO): The private partner designs, builds, finances, and operates the facility, while the public partner retains ownership.
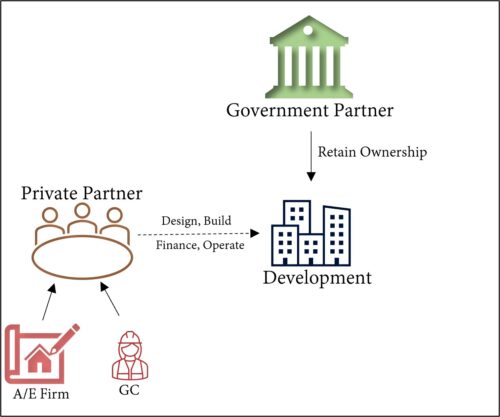
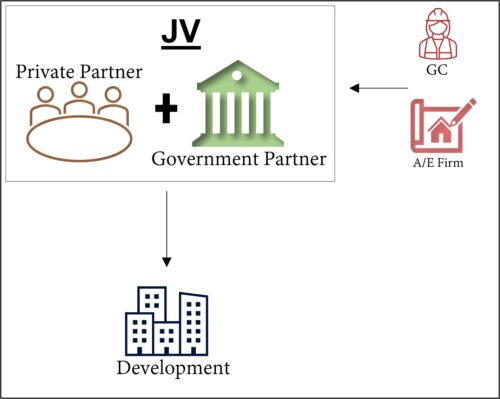
3. Joint Venture (JV): Both public and private partners jointly invest in and develop a project, sharing the risks and rewards.
Advantages of Public-Private Partnerships
There are several advantages of public-private partnerships, including:
Improved Efficiency
The private sector’s involvement can lead to better project management. Accordingly, it increases efficiency in the planning, constructing, and operating of public infrastructure.
Accelerated Project Delivery
By leveraging private sector resources, PPPs can expedite project delivery, reducing the time it takes to bring much-needed infrastructure and services to communities.
Risk Sharing
PPPs allow for the distribution of risk between public and private partners, reducing the burden on taxpayers and improving project outcomes.
Innovation
Private sector participation can result in innovative solutions as companies seek new ways to deliver projects more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Access to Capital
PPPs enable governments to tap into private-sector financing, reducing the strain on public budgets and allowing for more significant investment in essential infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Public-Private Partnerships
Despite their advantages, public-private partnerships also have some disadvantages:
Complexity
PPPs can be more complex than traditional procurement methods, requiring additional time and resources to negotiate and manage contracts.
Potential for Reduced Public Control
Governments may relinquish some control over the delivery of public services and infrastructure by involving private sector partners, potentially impacting service quality and accessibility.
Profit Motive
Private partners may prioritize profit over public interest, leading to concerns about PPP projects’ long-term sustainability and affordability.
Risk of Monopolies
PPPs can result in monopolistic situations, with a single private provider controlling access to essential public services, potentially leading to reduced competition and increased prices.
Examples of Public-Private Partnerships
In this section, we explore some notable examples of public-private partnerships:
Transportation Infrastructure
One of the most common areas for PPPs is transportation infrastructure. For instance, the construction of the Port of Miami Tunnel was a joint effort between the Florida Department of Transportation (FDOT) and Miami Access, (MAT). The project took five years to complete, and under the terms of the agreement, MAT will be responsible for operating the tunnel for the next 30 years in exchange for an annual availability payment. Additionally, this project was notable for being the second availability payment P3 initiative in the US to reach financial closure.
Energy Production
The Clean Energy Manufacturing Initiative (CEMI) is a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) wide commitment to innovation and breaking down market barriers. Subsequently, the objective is to enhance U.S. manufacturing competitiveness. As a result, CEMI’s Technologist in Residence (TIR) pilot is designed to accelerate strong national laboratory-industry relationships for Clean Energy Manufacturing. Therefore, these relationships will lead to high-impact, collaborative research and development. TIR will enhance the commercial impact of DOE’s national labs. In addition, it will develop mechanisms to help interested companies more easily connect and form relationships with DOE’s national labs.
Water and Sanitation
PPPs have also played a role in water and sanitation projects, such as the Vista Ridge Water Supply Project in San Antonio, TX. This project was designed and constructed for the Central Texas Regional Water Supply Corporation. It included the installation of 140 miles of transmission pipeline, three pump stations, and seven miles of well collection lines. As a result, the project will deliver 50,000 acre-feet of water per year.
Real Estate Development
Real estate development is another area where PPPs have been used effectively. One example is the Denver Union Station project in the United States, which involved redeveloping a historic railway station into a mixed-use transit hub.
PPPs in Real Estate Development
Public-private partnerships play a significant role in real estate development, allowing governments and private developers to collaborate on projects that benefit communities. Here, we discuss a few examples of real estate development public-private partnerships:
Hudson Yards, New York City
Hudson Yards is a large-scale mixed-use development built over a working rail yard in New York City. This project is a prime example of a PPP, with the city and state governments collaborating with private developers to create new residential, commercial, and public spaces.
Howard County Courthouse, Maryland
The Howard County Circuit Courthouse Project is a partnership between Edgemoor–Star America Judicial Partners and the government of Howard County, MD. The project is on an 18-acre site featuring a 230,000-square-foot LEED Silver circuit courthouse, a 691-space parking garage, and public outdoor space. In addition, the facility includes space for the State Attorney, Sheriff, Bar Association, Maryland Public Defender, and Clerk of Courts. Also included are office space and courtrooms for six judges, a large jury assembly area, a cafeteria, and a fitness center.
Alexandria Waterfront, Virginia
The Alexandria Waterfront is a $1 billion development that is being built on 13 acres of land along the Potomac River in Alexandria. The project is being developed by a joint venture between the city of Alexandria and private developers, the Carlyle Group and the Meridian Group. The project includes a mix of residential, commercial, and public space.
Balancing the Pros and Cons of PPPs
While public-private partnerships have numerous advantages, it is essential to balance the benefits and potential drawbacks. Governments must carefully consider the potential risks and ensure that contracts are structured to protect the public interest.
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
One crucial aspect of balancing the pros and cons of PPPs is ensuring transparency and accountability in project development and execution. This includes conducting thorough due diligence, engaging stakeholders, and providing regular updates on project progress.
Promoting Competition and Value for Money
To maximize the benefits of PPPs, governments should promote competition and ensure that projects deliver value for money. This can be achieved through competitive procurement processes and by conducting rigorous financial analysis to assess project viability.
Establishing a Robust Legal and Regulatory Framework
A strong legal and regulatory framework is essential for the success of PPPs. Governments must establish clear rules and guidelines to govern the development and operation of public-private partnerships, ensuring that both public and private partners are held accountable for their actions.
Public-private partnerships offer a unique opportunity for governments to collaborate with private sector entities to improve public services and infrastructure. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of PPPs, we can better appreciate their role in promoting economic growth and development. As long as governments carefully consider potential risks and implement robust legal and regulatory frameworks, PPPs can benefit communities significantly.
To learn the A/E company’s role in PPPs read The Power of Teamwork: Why Architects and Engineers are Key to MDAs